Customer service is rapidly evolving. Traditional chatbots and basic retrieval systems are no longer enough to meet modern expectations for accuracy, personalization, and speed. Businesses now need systems that can reason, retrieve, and act — not just answer questions.
This is where Agentic RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) comes in.
Agentic RAG combines large language models, retrieval systems, and autonomous agents to create customer service systems that can think through tasks, pull the right information, and take actions across tools and workflows.
In this guide, you’ll learn exactly how to deploy Agentic RAG for customer service automation, step by step, including architecture, tooling, data pipelines, evaluation, and real-world best practices.
What Is Agentic RAG (and Why It Matters for Customer Service)
Standard RAG systems retrieve documents and pass them to a language model to generate an answer. Agentic RAG goes further by adding autonomous decision-making and tool use.
Agentic RAG systems can:
- Decide what information to retrieve
- Break complex requests into subtasks
- Call APIs and internal tools
- Validate answers
- Escalate to humans when needed
- Update tickets, CRM records, or knowledge bases
For customer service, this means:
- Higher first-contact resolution
- Fewer hallucinations
- Automated workflows, not just answers
- Better personalization and context awareness
Instead of a static Q&A bot, you get a goal-driven AI agent.
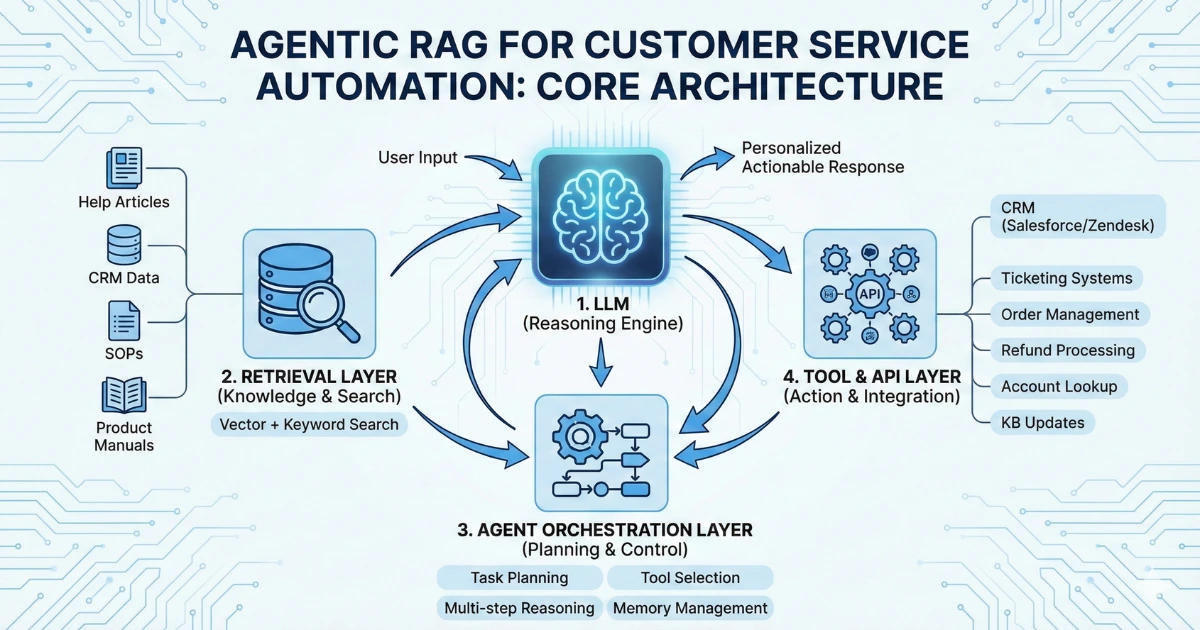
Core Components of an Agentic RAG System
Before deploying, you need to understand the architecture.
1. Large Language Model (LLM)
The reasoning engine that:
- Understands user intent
- Plans multi-step actions
- Generates responses
- Interprets retrieved context
Examples:
- GPT-style models
- Claude
- Open-source LLMs (LLaMA, Mistral, etc.)
2. Retrieval Layer (Vector + Keyword Search)
This is where knowledge lives.
Typical sources:
- Help center articles
- Internal SOPs
- CRM data
- Order and billing systems
- Policy documents
- Product manuals
Technologies:
- Vector databases (Pinecone, Weaviate, FAISS, Milvus)
- Hybrid search (BM25 + embeddings)
3. Agent Orchestration Layer
This is what makes it “agentic.”
Responsibilities:
- Task planning
- Tool selection
- Multi-step reasoning
- Memory management
- Error handling
Frameworks:
- LangChain Agents
- LlamaIndex Agents
- OpenAI Assistants-style tool calling
- Custom orchestration logic
4. Tool & API Layer
This enables action, not just answers.
Examples:
- CRM (Salesforce, HubSpot, Zendesk)
- Ticketing systems
- Order management systems
- Refund processing
- Account lookup
- Knowledge base updates
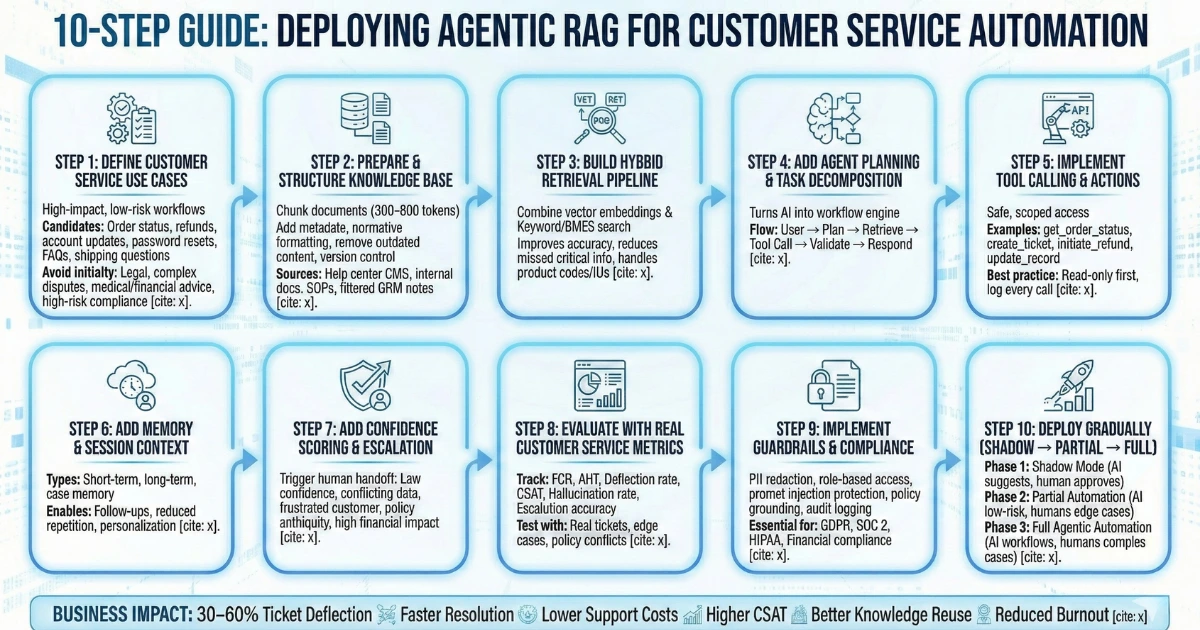
Step 1: Define Customer Service Use Cases
Start with high-impact, low-risk workflows.
Best candidates:
- Order status inquiries
- Refund and return policies
- Account updates
- Password resets
- FAQ resolution
- Knowledge base search
- Shipping and delivery questions
Avoid initially:
- Legal decisions
- Complex billing disputes
- Medical or financial advice
- High-risk compliance flows
Step 2: Prepare and Structure Your Knowledge Base
Agentic RAG is only as good as your data.
Best Practices for Knowledge Prep
- Chunk documents into 300–800 token segments
- Add metadata (category, product, date, region)
- Normalize formatting
- Remove outdated content
- Version control policies
Recommended Data Sources
- Help center CMS
- Internal Google Docs / Confluence
- SOP repositories
- CRM notes (carefully filtered)
Step 3: Build a Hybrid Retrieval Pipeline
Don’t rely on vectors alone.
Use Hybrid Search
Combine:
- Vector embeddings
- Keyword/BM25 search
Why:
- Improves accuracy
- Reduces missed critical info
- Handles product codes, SKUs, IDs
Step 4: Add Agent Planning and Task Decomposition
This is where Agentic RAG shines.
Instead of:
User → Retrieve → Answer
You get:
User → Plan → Retrieve → Tool Call → Validate → Respond
This turns your AI into a workflow engine,, not just a chatbot.
Step 5: Implement Tool Calling and Actions
Give your agent safe, scoped access.
Examples:
- get_order_status(order_id)
- create_support_ticket(user_id, issue)
- initiate_refund(order_id)
- update_customer_record()
Best practice:
- Use read-only tools first
- Add write actions gradually
- Log every tool call
Step 6: Add Memory and Session Context
Customer service depends on continuity.
Types of memory:
- Short-term (conversation context)
- Long-term (customer preferences, history)
- Case memory (open tickets, prior issues)
This enables:
- Follow-ups
- Reduced repetition
- Personalization
Step 7: Add Confidence Scoring and Escalation
Not every case should be automated.
Trigger human handoff when:
- Confidence score is low
- Conflicting data retrieved
- Customer is frustrated
- Policy ambiguity exists
- Financial impact is high
This protects customer experience and compliance.
Step 8: Evaluate with Real Customer Service Metrics
Don’t just test with generic NLP benchmarks.
Track:
- First Contact Resolution (FCR)
- Average Handle Time (AHT)
- Deflection rate
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT)
- Hallucination rate
- Escalation accuracy
Create test suites using:
- Real historical tickets
- Edge cases
- Policy conflicts
- Ambiguous queries
Step 9: Implement Guardrails and Compliance
Customer service automation needs controls.
Key guardrails:
- PII redaction
- Role-based tool access
- Prompt injection protection
- Policy grounding requirements
- Audit logging
This is essential for:
- GDPR
- SOC 2
- HIPAA (if applicable)
- Financial compliance
Step 10: Deploy Gradually (Shadow → Partial → Full)
Follow a phased rollout:
Phase 1: Shadow Mode
- AI suggests answers
- Human approves
Phase 2: Partial Automation
- AI handles low-risk flows
- Humans handle edge cases
Phase 3: Full Agentic Automation
- AI handles workflows
- Humans focus on complex cases
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Treating RAG as “set and forget”
- Using only vector search
- Allowing unrestricted tool access
- Ignoring evaluation pipelines
- Skipping human-in-the-loop early
- Poor knowledge base hygiene
Why Agentic RAG Outperforms Traditional Chatbots
Traditional bots:
- Answer questions
- Limited context
- No actions
- Rule-based flows
Agentic RAG systems:
- Reason through problems
- Take real actions
- Learn workflows
- Personalize responses
- Scale with business complexity
Business Impact of Agentic RAG for Support Teams
Companies deploying Agentic RAG report:
- 30–60% ticket deflection
- Faster resolution times
- Lower support costs
- Higher CSAT
- Better knowledge reuse
- Reduced human burnout
Frequently Asked Questions
Final Thoughts
Agentic RAG represents the next generation of customer service automation. It moves beyond static Q&A into goal-driven, tool-using AI agents that can resolve issues end-to-end.
If you want scalable, accurate, and workflow-aware customer support, deploying Agentic RAG is no longer optional — it’s a competitive advantage.







